The Trinomial System of Zoological Nomenclature
Formal categories
Genus
Used as a group for the most closely-related species.
Species
For the majority of distinguishable insect taxa a binomial system of formal names is applied. The species (abbreviated sp. or plural
spp.) name is always accompanied by the genus in documents. Sibling species are morphologically similar species that have been shown to represent distinct, reproductively-isolated
taxa. Their formal description is often avoided due to the difficulty of separating preserved specimens from other similar species.
Subspecies
The trinomial system may be applied to geographically distinguishable populations of a species, when subspecies (abbreviated
ssp.) are described. A subspecific name is added after the species name (+
author's name for the new subspecies name when first used). The original species is referred to as the nominotypical subspecies. The species name is repeated to indicate a trinomial status followed by that
author's name.
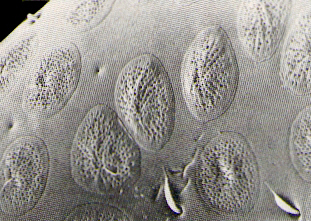
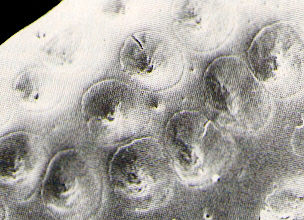
The differences between insect species can sometimes
only be observed using a
microscope.
Informal categories
Clines
A cline is a gradient in a measurable character within a species. Sometimes populations within a cline are given
subspecific, trinomial names. The term is most commonly applied to geographical variation when populations interbreed with neighbouring populations and show a gradual change, rather than an abrupt one.
Biotypes
Biotypes have no formal taxonomic status but they may be significant in biological control studies. The term refers to populations of a species which although morphologically indistinguishable, exhibit different biological characteristics. Quite often subsequent detailed studies reveal morphological differences in populations which enable their description as a separate species or subspecies.
[ Back ] [ Next ]
Don Sands
